Anterior-segment optical coherence tomography for tacrolimus therapy response monitoring of vernal keratoconjunctivitis
Medical hypothesis, discovery & innovation in optometry,
Vol. 3 No. 4 (2022),
14 January 2023
,
Page 152-159
https://doi.org/10.51329/mehdioptometry164
Abstract
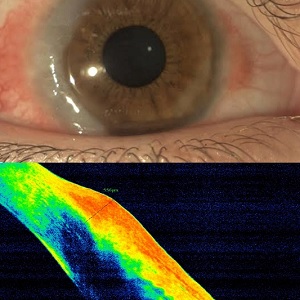
Background: Vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC), a chronic bilateral eye disease, is a severe form of allergic conjunctivitis. Anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) is a rapid, noninvasive, in vivo visualization modality for the anterior segment structures that has been used in diagnosing and staging diseases and assessing the treatment efficacy. We used anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) to monitor the efficacy of the tacrolimus eye ointment in managing VKC.Methods: In this prospective follow-up study, we included patients with active symptomatic VKC. All patients were treated with the 0.03% tacrolimus ophthalmic ointment twice daily for 2 months and then once daily for 1 month. All patients underwent AS-OCT before and 3 months after treatment as an objective method to assess the treatment efficacy.
Results: We included 20 eyes of ten patients (nine men and one woman) with active symptomatic VKC. The mean age was 17.3 (range: 11 – 36) years, with nine patients having a palpebral type and one patient having a mixed type of VKC. Substantial flattening and reduction in the papilla size were observed in all patients at the post-treatment follow-up. AS-OCT measurements revealed significant reductions in the vertical, horizontal, and total diameters of the palpebral papillae and limbal conjunctival thickness after 3 months of treatment compared to baseline measurements (all P < 0.001). No serious adverse effects attributable to tacrolimus administration were observed in the study period.
Conclusions: AS-OCT is a suitable objective method for evaluating the treatment efficacy of the 0.03% tacrolimus eye ointment in patients with VKC. Future large-scale studies including a wide range of age groups with longer follow-up periods and AS-OCT monitoring at multiple post-treatment visits are required to confirm our preliminary results. Moreover, the diagnostic accuracy of AS-OCT in monitoring patients with active VKC should be tested in comparison with objective scoring by an experienced corneal fellowship.
Keywords:
- tacrolimus anhydrous
- vernal keratoconjunctivitis
- optical coherence tomography
- papillae
- side effects
- palpebral conjunctiva
- bulbar conjunctiva
- Abstract Viewed: 0 times
- Full Text PDF Downloaded: 0 times