A prospective contralateral eye comparison of the tolerability of two artificial tears with different physical properties in patients with dry eye disease
Medical hypothesis, discovery & innovation in optometry,
Vol. 4 No. 1 (2023),
4 April 2023
,
Page 1-6
https://doi.org/10.51329/mehdioptometry167
Abstract
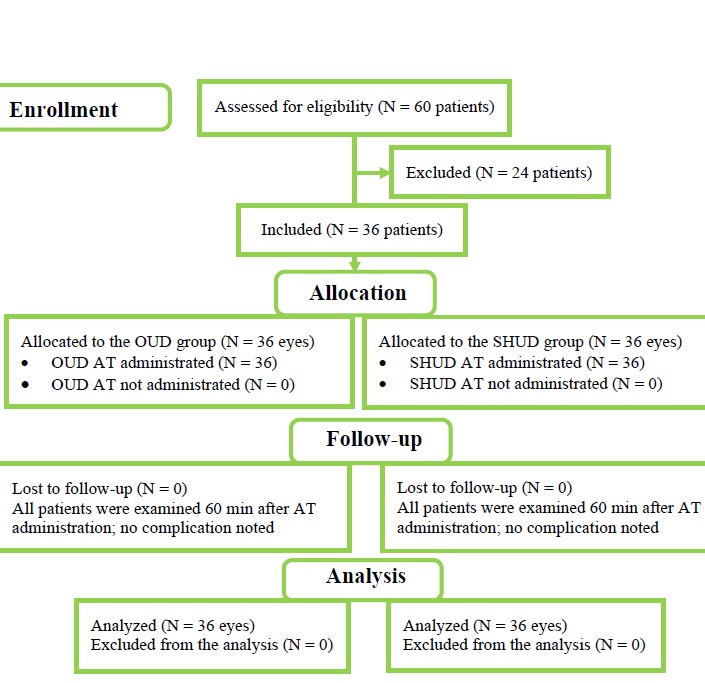
Background: Artificial tears (ATs) are widely used in ophthalmic practice with various formulations, mainly as a treatment for dry eye, owing to their rapid ability to alleviate the signs and symptoms of this condition. We aimed to investigate drop comfort and subjective ocular symptoms after instillation of the following ATs with different physical properties: Optive® non-preservative (OUD) and Systane® Hydration non-preservative (SHUD).Methods: This was a prospective, double-blind, randomized, contralateral eye comparison study. A rheometer and a digital pH meter were used to evaluate the viscosity and pH of both ATs prior to instillation. We recruited 36 patients with dry eye disease. Single standardized AT volumes were set using a micropipette for all patients. Ocular discomfort was assessed using the Ora Calibra™ Ocular Discomfort and 4-Symptom Questionnaire (OOD4SQ; 0 – 5 scale) before and 60 min after instillation. Drop comfort was assessed using the Ora Calibra™ Drop Comfort Scale (0 – 10 scale) immediately after AT instillation. The difference in the drop comfort score (DCS) between the two ATs and ocular discomfort scores using OOD4SQ before and 60 min after instillation of each AT were recorded and compared.
Results: The viscosities and pH of SHUD and OUD were 32.73 centipoise (cP) and 7.74 and 14.42 cP and 7.19, respectively. The mean (standard deviation) DCS was higher in the SHUD group than in the OUD group (1.83 [1.21] versus 1.67 [1.12]); however, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). There was a significant reduction in all parameters of OOD4SQ including overall discomfort, burning, dryness, grittiness, and stinging 60 min after OUD instillation (all P < 0.05), while a significant difference was only noted in dryness (P < 0.05) in the SHUD group.
Conclusions: OUD, which has a lower viscosity and pH compared to SHUD, provides less subjective sensation and better ocular comfort 60 min after instillation. Further randomized clinical trials including patients with dry eye disease of different severities, larger sample sizes, and longer follow-up periods are required to verify our findings.
Keywords:
- artificial tears
- viscosity
- dry eye disease
- ophthalmic absorption
- clinical efficacy
- prospective study
- Abstract Viewed: 0 times
- Full Text PDF Downloaded: 0 times